Any person, regardless of age, gender and status, can become a host and habitat for parasitic microorganisms. Although the word "host" is a strong word, because it is a worm that lives in the human body, absorbs its nutrients and energy, poisons the body and harms the body, causing some negative symptoms.
According to statistics from the World Health Organization, most people live with at least one type of parasite. And, in general, there are more than 70 species that can choose the human body as a home.
Some people think that parasites live exclusively in the intestines, while everyone remembers pinworms - small, white worms. But in reality, worms can penetrate any internal organ or system, as a result of which they interfere with its function, which is dangerous not only for human health, but also for his life.
It is necessary to consider what types of helminths are there, and which are the most common? At the same time, find out what symptoms indicate their presence, and what treatment will help to overcome the disease with the least danger to health?
Types of helminths, their classification
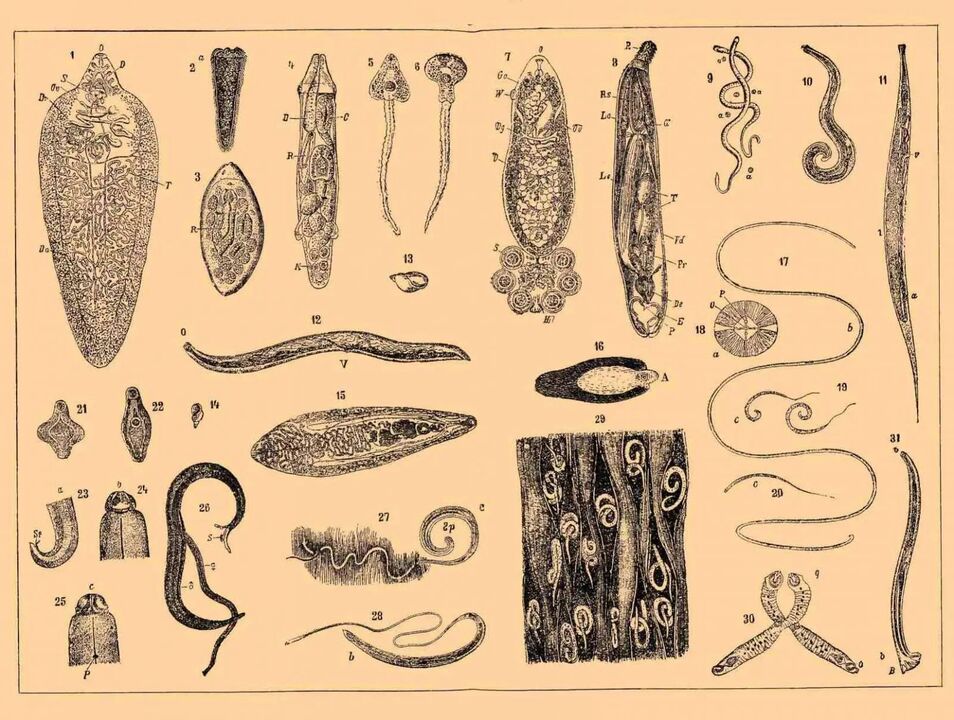
There are more than 300 species of parasites in the world, which belong to different classes and groups of microorganisms. In our country, only 70 species are found, and from this figure we can choose 10, which are found in most cases.
Parasitic worms, depending on the characteristics of their parasitism, can be divided into two groups - intestinal and tissue.
The first group chooses the human intestine as its home, and may include pinworms, roundworms, lamblia, hookworms, whipworms, bovine tapeworms, pig tapeworms and broad tapeworms.
Tissue groups include trematodes, trichinella, liverworms, echinococcus and alveococcus. They can settle in any internal human organ and stay there for years.
Depending on the life cycle of parasites (as well as the source of infection), they can be divided into the following types:
- Biohelminths - the eggs and larvae of this group of parasites mature in the organisms of animals (cows, dogs, cats) or insects (mosquitoes, flies). That is, human infection occurs directly from them. And transmission from one person to another is not possible.
- Geohelminths - the eggs and larvae of this group of parasites mature exclusively in the soil, that is, outside the human body.
- Parasite contact - infection occurs directly from a sick person to a healthy person (through handshakes, household items, bedding, etc. ).
Types of worms, depending on the class, are divided into the following types:
- Round parasites (nematodes) come in many sizes and shapes and are always different sexes. These include pinworms and roundworms (as in the photo).
- Cestodes or tapeworms are long worms that feed through their own integument. These include cattle and pig tapeworms (commonly found), and echinococcus (as in the photo).
- Trematodes or flukes - opisthorchiasis, schistosomiasis and some other types of parasitic microorganisms.
Tapeworms and worms are always parasites, but the group of roundworms has more than 10, 000 species, and only some of them can live in the human body.
Brief characteristics of common parasites
Pinworms, penetrating the human body, cause a disease called enterobiasis. It looks like a small and round worm, white or yellowish, with a maximum size of one centimeter.
Penetrating the human body, they settle in the intestines. Helminths are a type of contact parasite, that is, they can be transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person. At night, the female crawls out of the gut and lays eggs. As a result, the main symptom of this disease is unbearable itching in the anal area.
The life cycle of pinworms varies from 4 to 6 months. It is possible to get rid of it only when the last larva dies. Parasite eggs have amazing vitality and can adapt to any unfavorable conditions.
The most common parasites in the human body include the following types:
- Ringworm (ascariasis).
- Toxocara (toxocariasis disease).
- Whipworm (trichocephalosis).
- Trichinella (trichinosis).
- Tapeworm or bovine tapeworm (taeniarinhoz).
- Pig tapeworm (disease - taeniasis, cysticercosis).
Medical statistics say that broad tapeworms are quite common, which cause diseases such as diphyllobothriasis, as well as echinococcus (echinococcosis), cat fluke (opisthorchiasis), and lamblia - giardiasis.
All parasites, in the course of their life activity, have a negative effect on the human body, and the symptoms of each disease are significantly differentiated.
It should be remembered that the treatment also depends on the type of parasitic microorganisms, the intensity of the helminthic attack, and the number of helminths that have penetrated the human body.
Ascaris, Toxocara
Human roundworms are large round worms with curved (hook-like) ends. The size varies from 50 cm to one meter in length, and about 6 centimeters in diameter.
Male length is always smaller than female length. As a rule, the size of the male parasite does not exceed 25 centimeters. Ascaris larvae are relatively small in size. With the intensity of helminthic attacks, roundworms can multiply as quickly as possible, as a result of which parasitic balls are formed in the intestine.
Ascaris (as in the photo) belongs to geohelminths. Eggs can get from the soil into the small intestine, where they change over time into larvae, which, in a good environment, can penetrate the circulatory system, and from there, through the blood, move to all internal organs - the lungs, heart, kidney, cerebral hemisphere, skin, eye.
If the larvae settle in the lungs, they destroy the alveoli and enter the bronchi, and then, together with bronchial secretions, into the oral cavity, and again end up in the intestine. Therefore, secondary infection occurs. Adults can lay several thousand eggs per day and live inside the human body for several years. Symptoms of ascariasis:
- General malaise, weakness.
- More nervous.
- Increased body temperature.
- Shortness of breath, non-productive cough.
- Pain in the sternum.
Treatment of ascariasis involves initial cleansing of the body, doctors recommend taking laxatives and sorbents that help remove parasitic waste. Then anthelmintic drugs are prescribed, taking into account the age and weight of the patient, and the intensity of the helminthic attack.
Treatment of roundworms is advised with drugs that aim to destroy them.
Toxocara is a round parasite (as in the photo), yellow in color and up to 10 centimeters long. Infection occurs through contact with animals in most cases, you can get infected from cats and dogs.
The female parasite can produce up to 250 thousand eggs per day. Helminth eggs enter the human body through the oral cavity and then end up in the intestine. Their life cycle can be compared to a roundworm; they can also enter the circulatory system, and then into various internal organs.
In the human body, helminth larvae are unable to develop into adults; its maturation occurs exclusively in the intestines of animals. In the human body, larvae can live up to 10 years. The symptoms of toxocariasis vary significantly, all depending on the organ in which the larvae have settled. Common symptoms of this disease include:
- Allergic reactions in the form of rash, itching, redness of the skin.
- Shortness of breath, difficulty breathing.
- Appropriate non-productive cough.
- Wheezing when breathing.
The acute form of the disease has more "traditional" symptoms, which include weakness and apathy, fever, increased body temperature, joint and muscle pain, headache and dizziness.
Treatment of toxocariasis begins with etiotropic therapy, which directly affects the cause of the disease, namely the parasite larvae. Next, drugs are recommended to restore the function of the affected organs and systems.
Whipworm, Trichinella
In appearance, the whipworm is a thin worm, its approximate length is from 3 to 5 centimeters, its diameter is like a human hair. It has a sharp tip, where it is fixed in the intestinal mucosa.
Helminths can penetrate the human body from the soil, and then move to the intestines, where the larvae are formed. As a rule, this type of parasite resides in the cecum and appendix. Able to live in the human body for 3 to 4 years.
The peculiarity of infection with this parasite is that the disease can be asymptomatic. However, there are "classic" signs that are most often confused with respiratory diseases - cough, fever, nausea.
Whipworm reduces the body's defenses, as a result, against the background of its infection, a secondary infection can occur, which significantly worsens the patient's condition. The following clinical symptoms are distinguished:
- Pale skin.
- Weakness, nausea.
- Digestive tract disorders.
- Abdominal pain syndrome.
- There is a mixture of blood in the stool.
- Increased irritability, convulsive state.
- Headache and dizziness.
As a rule, it is quite rare to detect parasites in the early stages of infection. However, treatment must be comprehensive. It includes narrow-spectrum anthelmintic drugs that act exclusively on whipworms, pain relievers and antispasmodics.
Trichinella is a small worm no more than 5 millimeters long. Refers to biohelminths that circulate among predatory and domestic animals. Parasites can enter the human body along with animal flesh.
The female Trichinella ends up in the human small intestine, where the reproductive process takes place and new larvae emerge. These larvae enter the circulatory system and can spread throughout the human body through the bloodstream. Trichinella's "favorite" local area is skeletal muscle, where it can live up to 5 years. The first symptoms are observed in patients on the 8th-10th day of infection:
- Painful sensation in the abdominal area.
- Frequent nausea.
- Vomiting, digestive tract disorders.
- Loss of appetite.
After the larvae move throughout the body, the symptoms described above become more pronounced, with the addition of joint and muscle pain and allergic reactions (itching, hives, rash). If treatment is not started on time, this disease causes complications in the cardiovascular system, central nervous system and respiratory system.
Treatment includes anthelmintic drugs, as well as symptomatic therapy that combats allergic manifestations. At high temperature, antipyretic drugs are recommended. As a rule, therapy is carried out in a hospital setting.
Cattle and pig tapeworms
The bull tapeworm can reach a size of thirty meters, it has a small head, and there are thousands of segments on the body. There are 6 hooks on the head of the parasite. Helminth larvae develop in cattle. It can enter the human body through raw meat that is well processed with heat.
Throughout its life cycle, it remains in the small intestine, where it forms new segments. After that it is formed, and eggs are obtained from it. Each segment contains up to 100 thousand eggs.
The parasite eats the entire body surface and can live in the human body for up to 10 years. Common symptoms of this disease include:
- Systematic pain in the abdomen.
- Nausea.
- Loss of appetite, vomiting.
- Lose weight.
- Increased gas formation.
- Urges to defecate up to 5 times a day.
Treatment involves a health-enhancing diet that creates an unfavorable environment for the life of parasitic microorganisms, as well as anthelmintic drugs. Tablets are taken according to the regimen recommended by the doctor. After taking the medicine, the parasite dies and comes out naturally along with the feces.
Pig tapeworms are similar in appearance to cattle tapeworms, but differ in length - they can be no more than 5 meters. Infection can occur through consumption of raw meat, as well as from sick people. The life cycle of a tapeworm is 20-30 years. Parasites can cause two diseases:
- Cysticercosis, when larvae enter the body.
- Taeniasis - adults "live" in the body.
Cysticercosis occurs against the background of sharp headaches, epileptic seizures, various rashes on the skin, and pathological changes in the eyeball are observed. Symptoms caused by adult parasites:
- Allergic reactions, shortness of breath.
- Abdominal pain, disturbed stool.
- Loss of appetite, gastrointestinal disturbances.
- Sleep disturbances, nervousness, excitement.
Treatment of larvae is a long process. Single larvae are surgically removed, then anthelmintic drugs are prescribed.
To remove adults from the human body, narrow-spectrum antiparasitic drugs are prescribed, which have an adverse effect on certain types of parasites. After the tapeworm leaves the body, it is examined to rule out the possibility of body parts being found in the intestine.
As medical practice shows, treating parasitic diseases is easier than diagnosing them in the early stages. Given this situation, it is recommended to pay attention to the slightest pathological changes in your body and immediately see a doctor for adequate therapy. The video in this article will tell you about the types of parasites that live in humans.